Intelligence for Pinch Zone Management in Paper and Pulp Industry
The paper and pulp industry are so deeply woven into our daily lives that it’s almost impossible to imagine a day without its products. On average, an individual in the United States uses about 700 pounds of paper products annually. From the packaging of your morning cereal to the tissues you use, the books you read, and even the cardboard boxes delivering your online orders – these are all products of this industry. Its omnipresence underscores its critical role in modern life.
The very processes that manufacture these essential items, namely handling heavy machinery, high temperatures, and hazardous chemicals, are rife with risks that could lead to injury, fatality, or environmental harm if proper precautions aren’t taken. Prioritizing safety ensures the uninterrupted production of the goods we depend on, while protecting workers and maintaining the industry’s sustainability and efficiency. Without safety, the foundation of modern life built by the paper and pulp industry becomes precarious.
Summary
Why Safety is Non-Negotiable in Paper and Pulp Industry
The paper and pulp industry involves heavy machinery, hazardous chemicals, and high-temperature processes, making it prone to accidents. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, there were 10,000 recordable injuries in paper manufacturing in 2015. The industry is vulnerable to several safety events, including:
- Chemical spills and exposure: Hazardous substances like chlorine dioxide and sulfur compounds can pose serious health risks.
- Mechanical equipment accidents: Crushing, amputation, and electrocution risks are prevalent due to improper machine guarding and lockout/tagout failures.
- Fire and explosions: Fires in storage areas and explosions in boilers or digesters are common.
- Slips, trips, and falls: Poor housekeeping and working at heights contribute to these incidents.
- Noise and heat stress: Prolonged exposure to high noise levels and excessive heat can lead to hearing loss and heat-related illnesses.
Financial Implications
- The total cost of injuries in the industry, including direct and indirect costs, is enormous.
- Potential mill closures due to regulatory compliance could result in the loss of about 3,500 jobs, or 1.6% of total employment in the sectors studied.
- The cost associated with downtime due to these events is at least 10x larger than the direct consequence.
These statistics highlight the significant safety challenges and financial implications faced by the paper and pulp industry in the United States, emphasizing the need for a better approach to keep our people out of harm’s way.

Traditional Methods for Pinch Zone Management
Traditionally, pinch zones in the paper industry are areas where moving machinery parts can trap or crush body parts which are managed using a combination of safety measures, including:
- Physical Barriers: Guards, covers, and enclosures are installed to prevent access to pinch points during operation.
- Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedures: These procedures ensure that machinery is properly shut down and cannot be accidentally reactivated during maintenance or repair.
- Signage and Warnings: Clear visual warnings, including signs and color-coded markings, highlight pinch zones to alert workers.
- Training Programs: Education for identifying pinch zones and following safe work practices to avoid these hazardous areas.
- Safety Interlocks: Mechanical or electrical interlocks are used to stop equipment operation if a safety guard is removed or accessed.
- Inspection and Maintenance: Routine checks are carried out to ensure guards, interlocks, and other safety mechanisms are in good condition.
Identifying white Spaces to understand the safety measure gaps
Traditional methods of managing pinch zones in the paper industry, while effective to some extent, come with several limitations and gaps. One of our customers in the space faced the following challenges and looked at us to mitigate the same:
- Missed Early Warnings: Without real-time monitoring, equipment failures or hazardous conditions can go unnoticed until they cause damage or injury, leading to operational downtime and safety incidents.
- Reactive Safety Measures: Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) protocols often intervene after risks are identified, which means avoidable accidents or equipment damage may occur before action is taken.
- Oversights: It only humans err, especially when driven by stress, fatigue, or complacency, resulting in serious accidents.
- Static Safety Tools: Physical barriers and signs don’t evolve with dynamic work conditions, such as machinery upgrades or changes in layout, leaving blind spots in hazard prevention.
- No Data Utilization: Traditional methods fail to capture valuable data that could highlight recurring risks or inform smarter, more predictive safety strategies.
- Costly and Inefficient Processes: Frequent manual inspections and repeated training demand significant resources but don’t guarantee optimal outcomes, especially if the same issues persist.
- Bypassed Safeguards: Under pressure to meet deadlines safety measures could be bypassed, increasing the likelihood of accidents and compromising the overall safety culture.
These challenges are more than theoretical as they represent tangible risks to worker well-being and operational efficiency in the paper industry.
AI-Powered Pinch Zone Management: A Smarter, Safer Approach
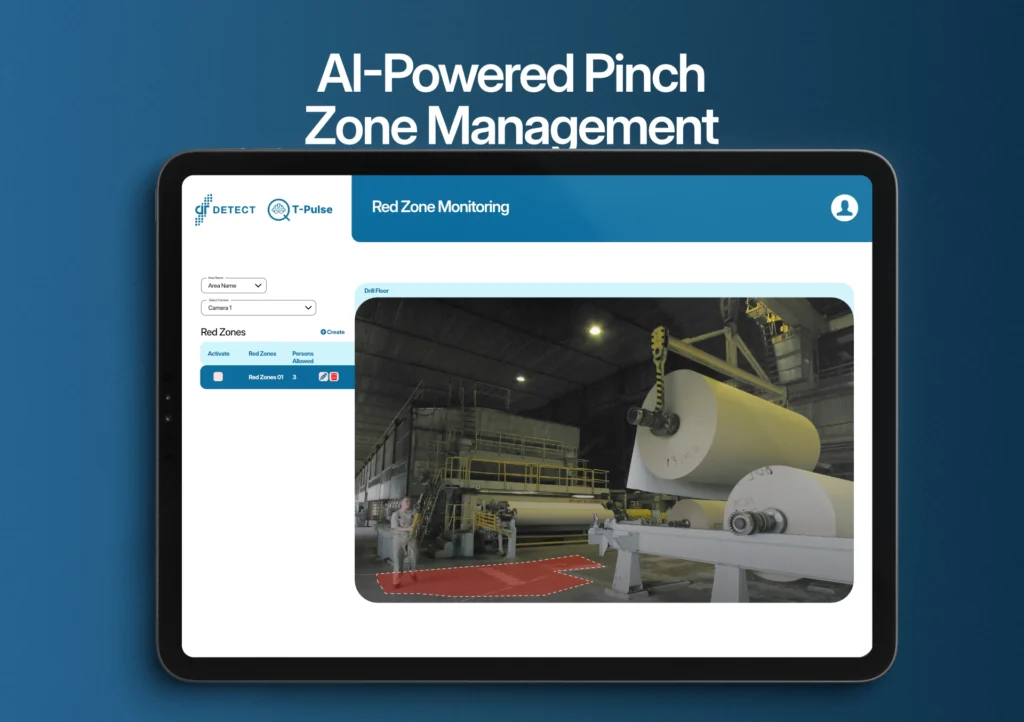
These gaps highlight the need for more advanced, dynamic, and data-driven solutions, like AI to supplement traditional methods and further enhance workplace safety. AI can address the shortcomings of traditional methods in managing pinch zones and workplace safety in the pulp and paper industry by offering innovative, dynamic, and proactive solutions:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Existing camera feeds can be continuously processed to monitor pinch zones, detecting hazardous conditions like unauthorized access or malfunctioning guards in real time, and instantly alerting workers and supervisors.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing data from machinery, AI can predict wear and tear or potential failures before they occur, preventing equipment-related accidents.
- Exposure Analysis: AI systems can evaluate movements and behavior to identify exposure to high-risk zones. These can then be controlled to prevent complacency resulting from “auto-pilot” mode of operation.
- Adaptive Systems: Unlike static safety measures, AI systems can dynamically adapt to changing work conditions, such as temporary removal of guards during maintenance, ensuring safety protocols remain in place.
By integrating AI into safety management, the industry can shift from reactive to proactive strategies, reducing incidents and fostering a safer work environment.
Prevention Through Control Systems
Control systems integrated with PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers) provide a robust mechanism for mitigating high-hazard conditions in the paper and pulp industry. These systems enable direct intervention to ensure worker safety and operational continuity. Key features include:
- Real-Time Hazard Responses: Cameras connected to control zones continuously monitor operations. If a person enters a red zone, the server triggers immediate actions such as activating alarms, slowing down machinery, or stopping it altogether.
- Automated Data Sharing: The system can program over 10 types of triggers, including SMS notifications, audible alarms, display alerts, dashboard updates, and email notifications. These ensure swift communication across teams to prevent accidents.
- Dynamic Safety Measures: By intertwining control systems with PLCs, machinery can be halted instantly during high-risk scenarios, reducing human error and ensuring compliance with safety protocols.
This integration enhances workplace safety by automating responses to hazards and enabling real-time decision-making.
Using Observations to Decrease Process Risks

Observation-based AI systems play a critical role in reducing risks by analyzing worker behavior and operational patterns. This approach focuses on:
- Behavioral Monitoring: Cameras connected to servers observe worker movements within control zones to identify unsafe practices or exposure to high-risk areas.
- Proactive Risk Mitigation: AI dynamically adapts safety measures based on observations, such as adjusting machine operations or restricting access to hazardous zones.
- Data-Driven Insights: Insights from observations are shared across dashboards for better decision-making and improved safety protocols.
By leveraging real-time observations and data analytics, companies can proactively address risks, optimize processes, and foster a safer workplace environment.
Measuring AI’s Effectiveness in Safety Management
Measuring the effectiveness of AI in workplace safety involves tracking various quantitative and qualitative metrics that assess improvements and outcomes. Here are some key metrics to consider:
- Reduction in Incident Rates: Number of accidents, injuries, or near-misses before and after AI implementation. Percentage decrease in specific types of incidents (e.g., pinch zone accidents).
- Response Time: Time taken to detect and address safety hazards or equipment malfunctions and emergency response triggered by AI alerts.
- Predictive Accuracy: Success rate of AI in predicting unsafe conditions or human errors. Frequency of false alarms versus accurate predictions.
- Compliance Rate: Percentage of adherence to safety protocols monitored by AI systems. Reduction in non-compliance incidents compared to manual checks.
- Downtime Reduction: Decrease in production interruptions due to timely maintenance predicted by AI. Efficiency in maintaining continuous operations without compromising safety.
- User Feedback: Employee perceptions of AI systems in improving safety and workflow. Increased confidence or trust in workplace safety measures.
- Safety Culture Improvement: Greater adoption of proactive safety practices among workers. Reduction in unsafe behaviors due to AI monitoring and feedback.
How T-Pulse Delivered Zero Incidents and 3x ROI for Our Client

Post Deployment the client was able to see results within a quarter
- Reduction in Incident Rates: Post implementation there were ZERO instances of unsafe human, machine interface within a quarter.
- Response Time: The response by the system was real time preventing issues in blind spots. The system blocked override attempt in 5 scenarios.
- Predictive Accuracy: The frequency of false alarms was eliminated to zero.
- Downtime Reduction: 17 trips were averted due to proactive detection
- User Feedback: Post implementation, the users on the ground became the biggest advocate for horizontal implementation.
The client achieved a 3x return through reduced downtime and by avoiding injuries.
The AI-Driven Path to Safety, Efficiency, and Innovation
AI integration in industrial settings offers a trio of opportunities: accelerating economic value, driving business growth, and fostering more creative and meaningful work for people. The integration of AI into industrial workplaces has proven transformative, bringing meaningful change by enabling smarter decision-making, enhancing safety, and optimizing efficiency.
Through real-time monitoring, predictive insights, and adaptive technologies, AI helps companies anticipate challenges before they escalate, reduce resource wastage, and cultivate a safer environment for workers. By embedding AI into daily operations, industries not only address longstanding inefficiencies but also pave the way for innovation and sustained growth.
By replacing static, reactive safety measures with dynamic, data-informed approaches, companies have significantly reduced workplace hazards, minimized downtime, and streamlined operations.
These advancements not only safeguard workers but also improve overall productivity, reinforcing the industry’s commitment to modernization and safety excellence. By leveraging AI for pinch zone management, our clients are improving their production processes, resulting in increased throughput, reduced waste, and improved energy efficiency.




